What is thyroid gland?
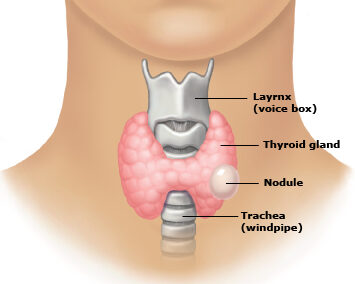
The thyroid gland is a small butterfly-shaped endocrine gland located in the front of the neck, just below the Adam’s apple. It plays a crucial role in the endocrine system by producing and secreting hormones that regulate various metabolic processes in the body.
The thyroid gland primarily produces two main hormones: triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4). These hormones are collectively known as thyroid hormones and are responsible for controlling the body’s metabolism, growth, and development. They regulate how the body uses energy, control the production of proteins, and affect the sensitivity of cells to other hormones.
The production of thyroid hormones is controlled by another endocrine gland called the pituitary gland, located at the base of the brain. The pituitary gland secretes a hormone called thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), which stimulates the thyroid gland to produce and release thyroid hormones in response to the body’s needs.
What are thyroid disorders?
Thyroid disorders can occur when the thyroid gland produces too much or too little thyroid hormone. Some common conditions include:
Hyperthyroidism: A condition in which the thyroid gland overproduces thyroid hormones, leading to an increased metabolic rate. Symptoms may include weight loss, rapid heartbeat, irritability, and heat intolerance. Graves’ disease is the most common cause of hyperthyroidism.
Hypothyroidism: A condition in which the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormones, resulting in a slowed metabolic rate. Symptoms may include fatigue, weight gain, depression, and cold intolerance. Hashimoto’s thyroiditis is the most common cause of hypothyroidism.
Goitre: Enlargement of the thyroid gland, often due to iodine deficiency or thyroid dysfunction. It can cause swelling in the neck and may lead to difficulty swallowing or breathing.
Thyroid cancer: Although relatively rare, thyroid cancer can develop in the cells of the thyroid gland. It often presents as a lump or nodule in the neck and may require surgical treatment.
What to do if I notice a thyroid lump?
If you discover a lump or swelling in your thyroid gland, it is important to seek medical attention promptly. While most thyroid nodules are noncancerous (benign), it’s crucial to have a healthcare professional like an Ear nose and Throat Surgeon with special interest in thyroid surgery to evaluate the lump to determine its nature and potential implications.
- Physical examination: The thyroid surgeon will perform a physical examination, palpating your neck to feel the size, texture, and characteristics of the lump. They may also evaluate your thyroid function by ordering blood tests to measure thyroid hormone levels and thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH).
- Diagnostic imaging: In many cases, further evaluation is necessary to determine the nature of the thyroid lump. Your healthcare provider may request imaging tests such as an ultrasound, which can help assess the size, location, and composition of the nodule.
- Fine-needle aspiration biopsy (FNA): Additional test like a fine-needle aspiration biopsy (FNA) may be recommended or done at the same time under guidance of the ultrasound based on the findings of the ultrasound. This procedure involves using a thin needle to extract a small tissue sample from the nodule for laboratory analysis. The biopsy results can help determine whether the nodule is benign or malignant.
- Follow-up and treatment: Depending on the results of the evaluation, the healthcare professional will discuss the appropriate course of action. Treatment options for thyroid nodules vary and may include watchful waiting (monitoring the nodule without immediate intervention), or surgery (partial or total thyroidectomy) if necessary.

Leave a Reply